- Genomics
- Transcriptomics
- Epigenomics
- Meta-omics
- Proteomics
- Single-Cell Sequencing
- Immune Repertoire Sequencing
- FFPE Samples

iTRAQ
Cases
Technical Information
Contact Us / Wish List
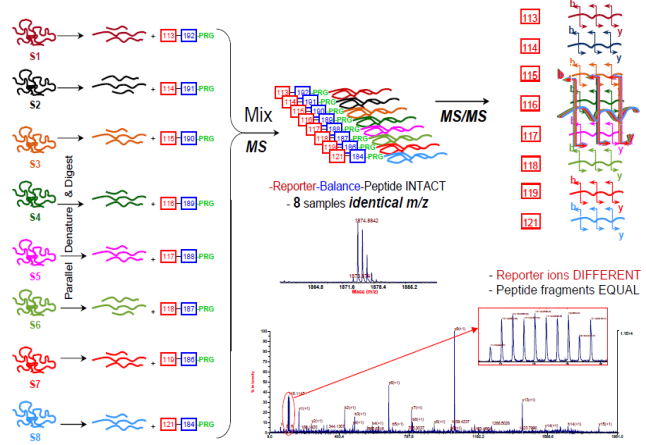 iTRAQ (isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation) is a non-gel-based technique used to quantify proteins from different sources in a single experiment. The method is based on the covalent labeling of the N-terminus and side-chain amines of peptides from protein digestions with tags of varying mass. The iTRAQ_8-plex_kit we provide can be used to label all peptides from different samples/treatments. These samples are then pooled and usually fractionated by nano liquid chromatography, followed by analysis using tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). A database search is then performed using the fragmentation data to identify the labeled peptides and hence the corresponding proteins. The fragmentation of the attached tag generates a low molecular mass reporter ion that can be used to relatively quantify the peptides and the proteins from which they originated.
iTRAQ (isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation) is a non-gel-based technique used to quantify proteins from different sources in a single experiment. The method is based on the covalent labeling of the N-terminus and side-chain amines of peptides from protein digestions with tags of varying mass. The iTRAQ_8-plex_kit we provide can be used to label all peptides from different samples/treatments. These samples are then pooled and usually fractionated by nano liquid chromatography, followed by analysis using tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). A database search is then performed using the fragmentation data to identify the labeled peptides and hence the corresponding proteins. The fragmentation of the attached tag generates a low molecular mass reporter ion that can be used to relatively quantify the peptides and the proteins from which they originated.
Benefits:
- Achieve identification and quantitation of multiple samples simultaneously, allowing up to eight samples to be compared at once.
- High diversity of proteins observed, including acidic, basic, high molecular weight (MW), low MW, and hydrophobic membrane proteins.
- High resolution and sensitivity, ensuring that both abundant and scarce proteins can be identified.
Identification of Novel Biomarkers for Sepsis Prognosis via Urinary Proteomic Analysis Using iTRAQ Labeling and 2D-LC-MS/MS. Plos one. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054237 (2013).
 Sepsis is a major cause of death for critically ill patients. The purpose of this study was to screen potential biomarkers for early prognostic assessment of patients with sepsis. For the discovery stage, 30 sepsis patients with different prognoses were selected. Urinary proteins were identified using isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) coupled with LC-MS/MS. Mass spec instrument analysis were performed with Mascot software and the International Protein Index (IPI); bioinformatic analyses were used by the algorithm of set and the Gene Ontology (GO) Database. For the verification stage, the study involved another 54 sepsis-hospitalized patients, with equal numbers of patients in survivor and non-survivor groups based on 28-day survival. Differentially expressed proteins were verified using Western Blot. A total of 232 unique proteins were identified. Proteins that were differentially expressed were further analyzed based on the pathophysiology of sepsis and biomathematics. For sepsis prognosis, five proteins were significantly up-regulated: selenium binding protein-1, heparan sulfate proteoglycan-2, alpha-1-B glycoprotein, haptoglobin, and lipocalin; two proteins were significantly down-regulated: lysosome-associated membrane proteins-1 and dipeptidyl peptidase-4. Based on gene ontology clustering, these proteins were associated with the biological processes of lipid homeostasis, cartilage development, iron ion transport, and certain metabolic processes.
Sepsis is a major cause of death for critically ill patients. The purpose of this study was to screen potential biomarkers for early prognostic assessment of patients with sepsis. For the discovery stage, 30 sepsis patients with different prognoses were selected. Urinary proteins were identified using isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) coupled with LC-MS/MS. Mass spec instrument analysis were performed with Mascot software and the International Protein Index (IPI); bioinformatic analyses were used by the algorithm of set and the Gene Ontology (GO) Database. For the verification stage, the study involved another 54 sepsis-hospitalized patients, with equal numbers of patients in survivor and non-survivor groups based on 28-day survival. Differentially expressed proteins were verified using Western Blot. A total of 232 unique proteins were identified. Proteins that were differentially expressed were further analyzed based on the pathophysiology of sepsis and biomathematics. For sepsis prognosis, five proteins were significantly up-regulated: selenium binding protein-1, heparan sulfate proteoglycan-2, alpha-1-B glycoprotein, haptoglobin, and lipocalin; two proteins were significantly down-regulated: lysosome-associated membrane proteins-1 and dipeptidyl peptidase-4. Based on gene ontology clustering, these proteins were associated with the biological processes of lipid homeostasis, cartilage development, iron ion transport, and certain metabolic processes.
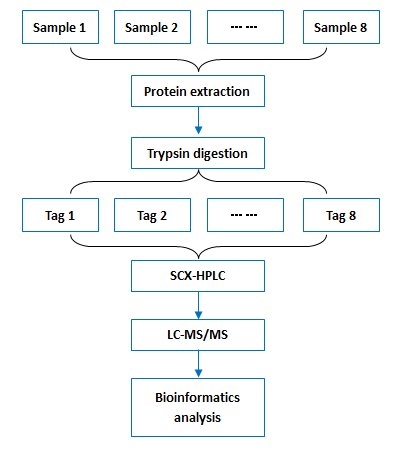
Workflow:
Bioinformatics:
Standard Bioinformatics Analysis
- Data statistics
- Protein identification by searching against database using MASCOT
- Protein quantification
Advanced Bioinformatics Analysis
- Protein GO category analysis
- Protein COG category analysis
- Protein pathway analysis
- Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) GO enrichment analysis
- DEPs pathway enrichment analysis
- Repeatability analysis
- Expression pattern cluster analysis (no less than three samples)
Custom Bioinformatics Analysis
Sample Requirements
|
Sample Type |
Amount of Sample required |
Comment(s) |
|
Fresh animal tissue (wet weight) |
≥ 100 mg |
For tissue with high impurity or low amount of proteins such as plant root or phloem, 5g sample is needed. |
|
Fresh plant tissue or fungus (wet weight) |
≥ 1 g |
|
|
Microorganism (e.g. bacteria) |
≥ 200 mg |
|
|
Cell |
≥ 3-5×106 cells |
For phosphorylated protein identification, the cell number should be more than 107. |
|
Blood |
Serum / plasma ≥ 500 µl Whole blood ≥ 5 ml |
We do not recommend sending whole blood sample because blood cells can be broken during transport process. |
|
Please remove high-abundance protein before sending extracted proteins and attach gel images before and after the removal of high-abundance protein. |
||
|
Body fluid (e.g. saliva and cerebrospinal fluid) |
≥ 5 ml |
/ |
|
Urine |
≥ 50 ml |
Centrifuge at 1000g for 5min to discard the precipitate before sending your sample to BGI Tech. |
|
Protein extract |
≥ 500 µg (concentration ≥1mg/ml) |
/ |

