
Whole Genome Mapping
Cases
Technical Information
Contact Us
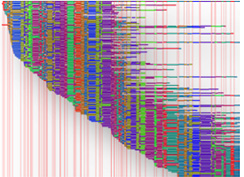 A Whole Genome Map is a high-resolution, ordered, whole genome restriction map generated from single DNA molecules extracted from bacteria, yeast, or other fungi. Whole Genome Mapping is a novel technology with unique capabilities in the field of microbiology, with specific applications in the areas of Comparative Genomics, Strain Typing, and Whole Genome Sequence Assembly. Whole Genome Maps are generated de novo, independent of sequence information, require no amplification or PCR steps, and provide a comprehensive view of whole genome architecture. A Whole Genome Map is displayed in the MapCode pattern where the vertical lines indicate the locations of restriction sites, and the distance between the lines represent the restriction fragment size.
A Whole Genome Map is a high-resolution, ordered, whole genome restriction map generated from single DNA molecules extracted from bacteria, yeast, or other fungi. Whole Genome Mapping is a novel technology with unique capabilities in the field of microbiology, with specific applications in the areas of Comparative Genomics, Strain Typing, and Whole Genome Sequence Assembly. Whole Genome Maps are generated de novo, independent of sequence information, require no amplification or PCR steps, and provide a comprehensive view of whole genome architecture. A Whole Genome Map is displayed in the MapCode pattern where the vertical lines indicate the locations of restriction sites, and the distance between the lines represent the restriction fragment size.
Benefits:
With Whole Genome Mapping, you will be able to investigate microbial structure, function, diversity and genetics— without the need for amplification, PCR, cloning, paired-end libraries, pure isolates, or genomic specific reagents. Using OpGen’s unique de novo Whole Genome Mapping Technology, the Argus Whole Genome Mapping System, BGI delivers high resolution, ordered whole genome restriction maps from single microbial DNA molecules.
Applications:
- Comparative Genomics
- Whole Genome Sequencing Assembly
- Strain Typing
Assisting Bacteria Genome Assembly - The Aacinetobacter baumannii Case
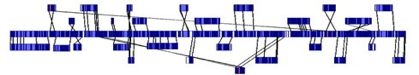
In this case, unordered contigs were aligned to the matching regions on the Whole Genome Map. Alignment lines are drawn between compared Whole Genome Maps to show placement. Crossing alignment lines indicate reverse orientation. The Gap sizes and locations (white colored) are visualized and enable further targeted analysis for whole genome closure.
Comparison of Assembly Performance Among Three Methods:
Method 2 combines Whole Genome Mapping and Solexa reads assembly, bringing the number of scaffolds to 1. It works better than method 1 and 3 which use large and small fragments to assemble without Whole Genome Mapping.
| Method | Number of scaffolds | Scaffold total length | Total length of outer gaps and inner gaps | Contig length/ genome length (%) |
| Assembly (short library reads only) | 88 | 4,060,072 | 309,996 | 85.88% |
| Assembly (short reads) + Whole Genome Mapping | 1 | 4,292,545 | 426,960 | 90.05% |
| Assembly (short reads + longer reads) | 74 | 4,366,732 | 307,400 | 92.96% |
Bioinformatics:
- Enzyme digestion result
- Assembly and analysis
- Whole Genome Map
- Scaffold placement
- Comparative genomics
- Strain typing
Sample Requirements:
- Sample condition: Bacteria DNA with size≥150Kb
- Sample concentration: 5-10 DNA/ image
We suggest sending bacterial cultural plate. For bacterial cultural plate, two more control plates are needed for re-culture. Label the culture condition and pathogenicity.
For pathogenic bacteria, suggest sending Bacteria Plug.

