
Animal / Plant

Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized plant and animal research, allowing us to decode the whole genomes of many species. NGS also enables us to detect functional genes and markers of important traits to facilitate molecular breeding and improve agriculture production and conservation. BGI has been a pioneer in this field and is highly experienced in applying NGS to the study of plant and animal genomes, with state-of-the-art technologies and computing power, rapid turn-around time, as well as strong bioinformatics know-how. To date, BGI Tech has sequenced 656 plant and animal reference genomes, including 421 animal genomes and 235 plant genomes.
BGI offers NGS services that enable you to:
- Study evolution and diversity using whole genome sequencing and transcriptome sequencing
- Accelerate molecular breeding with genotyping by sequencing and QTL mapping
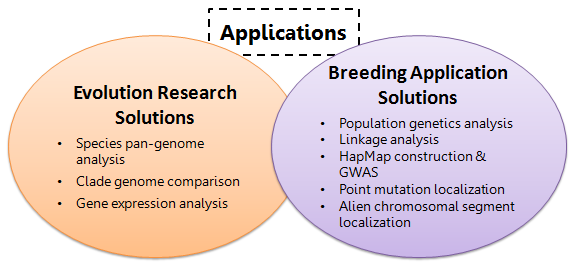
Figure 1. Applications of genome sequencing for plants and animals.
Evolution and Diversity:
De novo sequencing allows you to study genomes within the same species (Species Pan-genome) or decode genomes in the same family or genus (Clade Genomes). Population evolution based on whole-genome re-sequencing can be used for phylogenetic, linkage disequilibrium, genetic structure analyses, as well as population genetic structure and species formation, to explore mechanisms of biological evolution. Discovering the secrets of biological evolution will clarify the origin of species and the diversity of life on earth.
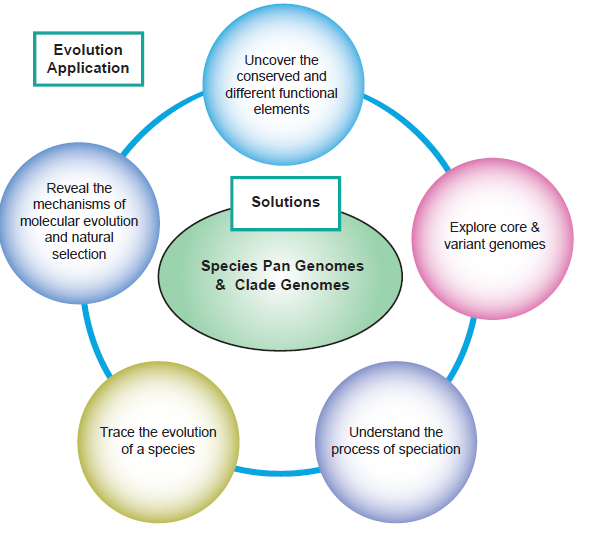
Figure 2. Evolution research based on de novo sequencing.
In addition to genomics, whole transcriptome analyses are very important to understanding how altered expression of genetic variants contributes to complex plant phenotypes. BGI offers an extensive service portfolio for gene expression analyses, from transcriptome sequencing (including miRNA and noncoding RNA analyses) to epigenomics research.
Molecular Breeding:
Molecular breeding applies molecular biology tools to accelerate the breeding process. One of the most important molecular breeding methods is marker-assisted selection (MAS), the use of tightly linked DNA markers that target loci as a substitute to assist in phenotypic screening. Recent improvements in NGS have simplified the discovery of DNA markers, making it much more cost-effective. As the largest genomics center in the world, BGI Tech has developed new services that advance NGS applications in the molecular breeding area. With our services, scientists can complete their breeding projects, which would take six to eight years using traditional strategies, in just one year. Our approach provides dramatic time and financial savings.
Research strategy
Figure 3. Research strategies of molecular breeding
Currently, genotyping by sequencing (GBS) is becoming increasingly important as a unique, cost-effective tool for associate studies and genomics-assisted breeding, particularly in plant species with complex genomes that lack a reference sequence. The key components of this system include reduced sample handling, fewer PCR and purification steps, no size fractionation, and inexpensive barcoding.
Advantages of GBS
- Faster, simpler protocol than traditional methods
- Simplified computational analyses
- High accuracy of SNP calling
- Low cost makes it an attractive option for large numbers of markers or individuals
- Decreased amounts of input DNA
Example - Cucumis melon breeding
Background
Melon (Cucurbitaceae cucumis) is cultivated worldwide and is an important agricultural crop. China has the largest cultivation region and the highest yield in the world. Although numerous varieties of melon have been developed through traditional crossbreeding techniques, shortcomings and deficiencies remain. While maintaining the yield of hybrid and wide adaptability traits, we directionally improved other traits, including background peel and flesh color. We helped scientists generate several new varieties that combined the desired traits of the parents.
Research strategy and results
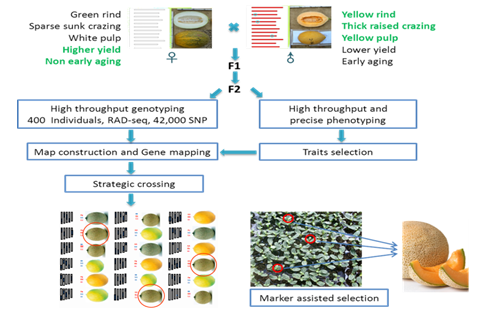
We obtain an improved variety with yellow rind, thick crazing, yellow pulp, and higher yield using NGS-based molecular breeding.
To learn more, please download the technical brochure Next Generation Sequencing in Plant and Animal Research.

